Understanding Compound Adjectives in English
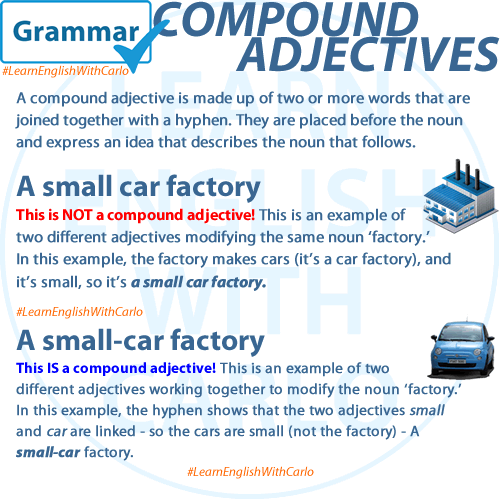
Compound adjectives are a fascinating aspect of English grammar that allow us to express detailed ideas about nouns in a concise and efficient way. As the name suggests, a compound adjective is made up of two or more words that work together as a single unit to describe a noun. These words are typically joined with a hyphen and placed directly before the noun they modify. By doing this, compound adjectives create a singular, unified description of the noun.
How Compound Adjectives Work
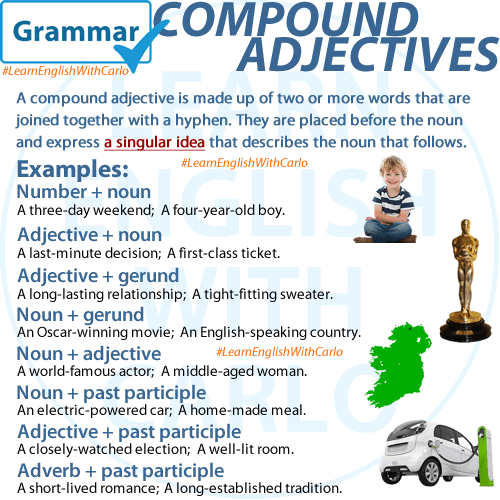
Compound adjectives combine words in a variety of patterns to convey specific meanings. Below are common structures of compound adjectives, along with examples to help clarify their usage.
1. Number + Noun
When a number and a noun combine to describe a specific quantity or measurement, they form a compound adjective:
- A three-day weekend
- A four-year-old boy
- A five-star hotel
Note: The noun in the compound adjective is always singular, even if the number indicates plurality.
2. Adjective + Noun
An adjective and a noun can team up to describe a noun:
- A last-minute decision
- A first-class ticket
- A high-speed train
3. Adjective + Gerund (-ing form)
An adjective combined with a gerund often describes the nature or effect of the noun:
- A long-lasting relationship
- A tight-fitting sweater
- A slow-moving vehicle
4. Noun + Gerund (-ing form)
A noun and a gerund together often indicate a function or characteristic:
- An Oscar-winning movie
- An English-speaking country
- A record-breaking performance
5. Noun + Adjective
A noun and an adjective can combine to describe a noun in a unique way:
- A world-famous actor
- A thirst-quenching drink
- A sugar-free dessert
6. Noun + Past Participle
A noun and a past participle often indicate what the noun is made of or its defining characteristic:
- An electric-powered car
- A homemade meal
- A sun-dried tomato
7. Adjective + Past Participle
An adjective combined with a past participle describes the state or condition of the noun:
- A closely-watched election
- A well-lit room
- A highly-respected professor
8. Adverb + Past Participle
When an adverb modifies a past participle, it gives additional nuance to the description:
- A short-lived romance
- A long-established tradition
- A fully-equipped kitchen
Important Notes on Compound Adjectives
- Hyphenation Matters: The hyphen is essential in compound adjectives. Without it, the meaning can become unclear or entirely different. For example:
- A small-business owner (a person who owns a small business)
- A small business owner (a short person who owns a business)
- Placement in a Sentence: Compound adjectives are typically placed before the noun they modify. When placed after the noun, they often lose the hyphenation and become part of a predicate.
- Before the noun: A well-known artist
- After the noun: The artist is well known.
- Not All Need Hyphens: If the compound adjective uses an adverb ending in -ly, the hyphen is not used:
- A beautifully designed room
- A carefully prepared presentation
Additional Examples
- A cold-blooded animal (Adjective + Past Participle)
- A two-story house (Number + Noun)
- A hand-painted vase (Noun + Past Participle)
- A quick-thinking detective (Adjective + Gerund)
Conclusion
Compound adjectives are a powerful tool for adding precision and variety to your writing. By understanding the structures and rules that govern their formation, you can use them effectively to convey specific and vivid ideas. With practice, you’ll find that compound adjectives are not only practical but also an enjoyable aspect of English to explore and master!