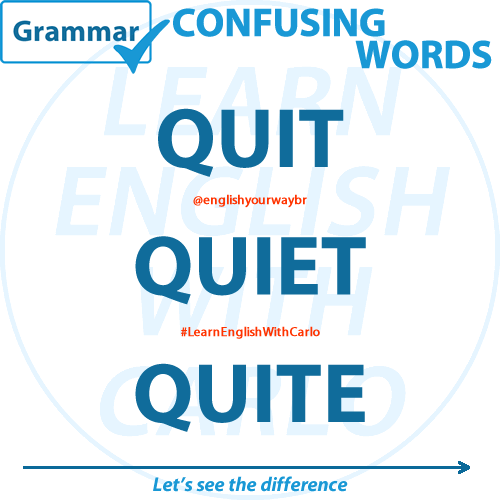
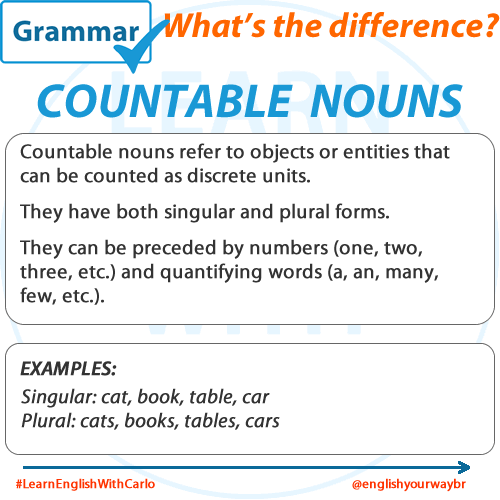
The best source of English Language material for all levels, from beginners to advanced students.
Let’s get started!
GRAMMAR GUIDE
In this comprehensive guide, I’ll break down the essentials of English grammar and provide you with tips and resources to help you become a grammar pro.
PDF DOWNLOADS
This series of 51 mini-lessons is designed to help you build a strong foundation in English. Each mini-lesson is available as a free PDF download and includes explanations, examples, and practice exercises. Whether you’re a student learning on your own or a teacher looking for classroom-ready material, these resources are free to use, print, and share. Enjoy your studies and keep practicing!
PRONUNCIATION GUIDE
For ESL (English as a Second Language) learners, mastering pronunciation is not just about speaking clearly; it’s about confidence and effective communication.
VOCABULARY GUIDE
In this section, we will explore the rich and diverse world of English vocabulary, equipping you with the words and phrases you need to express yourself accurately and confidently. Divided into specific pages to help whether you’re a beginner looking to master basic terms or an advanced learner.
EXERCISES
Test your knowledge of English with more than 50 interactive quizzes on a variety of grammar and vocabulary topics.
TIPS FOR IMPROVEMENT
Here you can find suggestions of things you can do daily to help you on the road to English Fluency. Learn how to improve your GRAMMAR, LISTENING, READING, and SPEAKING with these helpful tips.
READING COMPREHENSION
Here, you’ll find a variety of short stories accompanied by an interactive comprehension exercise. I’ll be adding more stories, so check back often.
INSTAGRAM BLOG
Connect with me on my popular Instagram for daily English learning content — grammar explanations, vocabulary boosts, pronunciation practice, and helpful study tips designed for English learners at all levels. Many of the ideas for the posts come from my students. Link: @englishyourwaybr