The subjunctive mood in English is used to express wishes, suggestions, demands, or hypothetical situations. It often appears after certain verbs (like “suggest” or “recommend”) and is characterized by using the base form of the verb, even with singular subjects (e.g., “I suggest that he go“). It can also express unreal or hypothetical situations, particularly …
Category: GRAMMAR
Permanent link to this article: https://englishyourway.com.br/grammar-subjunctive/
Oct 18
GRAMMAR – Modal Verbs
What Are Modal Verbs? Modal verbs are auxiliary (helping) verbs that express possibility, necessity, ability, permission, and other attitudes toward the action of the main verb. Unlike regular verbs, modal verbs do not change form based on the subject (e.g., “I can,” “he can”). They are always followed by the base form of the main …
Permanent link to this article: https://englishyourway.com.br/grammar-modal-verbs/
Oct 16
Turning Adjectives into Verbs with “-en”
In English, some adjectives can be turned into verbs by adding the suffix -en. These verbs usually indicate the process of becoming or making something have the quality described by the adjective. Understanding how and when to use -en to form verbs can greatly expand your vocabulary and improve your communication skills. How Does It …
Permanent link to this article: https://englishyourway.com.br/turning-adjectives-into-verbs-with-en/
Oct 15
Uses of “Off” as a Preposition
The preposition “off” has many different uses in English, depending on the context. Here’s a breakdown of its main uses: 1. Separation or Removal 2. Starting Point (in Time or Space) 3. Away from Work or Duty 4. Deactivation or Disconnection 5. Distance or Separation 6. Reduced or Discounted 7. Cancellation or Suspension 8. Condition …
Permanent link to this article: https://englishyourway.com.br/uses-of-off-preposition/
Oct 12
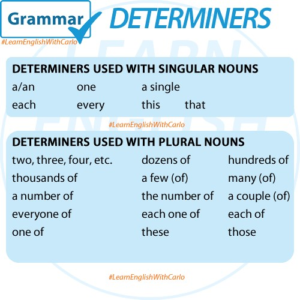
GRAMMAR – Determiners
Determiners are words that come before a noun to clarify what the noun refers to. They help specify whether we’re talking about something specific or general, countable or uncountable, and they can show possession, quantity, or definiteness. Mastering the use of determiners is key to sounding more fluent and accurate in English. Types of Determiners …
Permanent link to this article: https://englishyourway.com.br/grammar-determiners/
Oct 11
GRAMMAR – Pronouns (and adjectives)
Personal pronouns and possessive adjectives are essential elements of English grammar. They help us talk about people, things, and ownership without repeating the same nouns over and over again. In this post, we’ll explore five key types: subject pronouns, object pronouns, possessive adjectives, possessive pronouns, and reflexive pronouns. Understanding how to use each one correctly …
Permanent link to this article: https://englishyourway.com.br/grammar-pronouns-and-adjectives/
Permanent link to this article: https://englishyourway.com.br/grammar-more-confusing-words/
Permanent link to this article: https://englishyourway.com.br/grammar-migrate-vs-emigrate-vs-immigrate/
Oct 07
Present Perfect vs. Present Perfect Continuous
The Present Perfect and Present Perfect Continuous tenses can sometimes be used interchangeably, but they often emphasize different aspects of an action. Here’s a breakdown of when they are the same and when they are different: When the Present Perfect and Present Perfect Continuous Are the Same: Both tenses can be used to talk about …
Permanent link to this article: https://englishyourway.com.br/present-perfect-vs-present-perfect-continuous/
Oct 07
Understanding Ability in English: CAN, COULD, and WILL BE ABLE TO
In English, we use different forms to express someone’s ability to do something, whether in the present, past, or future. Let’s explore how CAN, COULD, and WILL BE ABLE TO are used to talk about ability. 1. CAN – Ability in the Present We use CAN to show that someone has the ability to do …
Permanent link to this article: https://englishyourway.com.br/ability-can-could-will-be-able-to/