Here are 9 parts of speech in English with definitions and examples.

NOUN
A noun is a word used to identify a person, place, thing, or idea. Nouns are the basic building blocks of sentences and are essential for communication in any language. Examples of nouns include “dog,” “car,” “teacher,” “city,” and “happiness.” Nouns can be singular or plural, and they can also be concrete (tangible objects) or abstract (ideas or concepts). In sentences, nouns often serve as the subject or object, providing clarity and context to the meaning of the sentence.
Examples:
Book (thing) – “She enjoys reading books in her free time.”
Teacher (person) – “The teacher explained the lesson clearly.”
Love (idea) – “Their love for each other grew stronger over time.”
PRONOUN
A pronoun is a word that takes the place of a noun in a sentence. Pronouns are used to avoid repetition and make sentences less cumbersome. They refer back to a previously mentioned noun or group of nouns and help maintain clarity and flow in writing and conversation. Examples of pronouns include “he,” “she,” “it,” “they,” “we,” and “you.” Pronouns can function as subjects, objects, possessives, or reflexives in sentences.
Examples:
He (subject pronoun) – “He went to the store to buy groceries.”
They (subject pronoun) – “They are going to the park this afternoon.”
I (subject pronoun); Her (object pronoun) – “I gave the book to her.”
VERB
A verb is a word that expresses an action, occurrence, or state of being in a sentence. Verbs are essential components of sentences as they convey the action or existence of the subject. They can describe physical actions (e.g., run, jump, eat), mental actions (e.g., think, believe, remember), states of being (e.g., is, are, was), or changes that occur (e.g., become, grow). Verbs can also indicate tense, showing whether an action is happening in the past, present, or future. In English, verbs are conjugated to match the subject in terms of person, number, and tense.
Examples:
Run (physical action) – “She runs in the park every morning.”
Think (mental action) – “He thinks before making a decision.”
Is (state of being) – “The cat is sleeping on the windowsill.”
ADJECTIVE
An adjective is a word that describes or modifies a noun or pronoun by providing more information about its qualities, characteristics, or attributes. Adjectives help to make descriptions more vivid and detailed, allowing us to express our thoughts more precisely. They can describe various aspects such as size, color, shape, age, origin, material, or purpose. Adjectives are essential for enriching language and making communication more expressive. Examples of adjectives include “big,” “red,” “round,” “old,” “Italian,” “wooden,” and “useful.”
Examples:
Big (describing size) – “The elephant is a big animal.”
Red (describing color) – “She wore a red dress to the party.”
Happy (describing emotion) – “They felt happy after winning the game.”

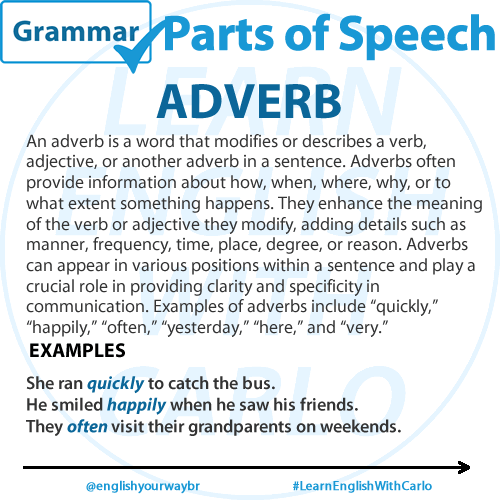
ADVERB
An adverb is a word that modifies or describes a verb, adjective, or another adverb in a sentence. Adverbs often provide information about how, when, where, why, or to what extent something happens. They enhance the meaning of the verb or adjective they modify, adding details such as manner, frequency, time, place, degree, or reason. Adverbs can appear in various positions within a sentence and play a crucial role in providing clarity and specificity in communication. Examples of adverbs include “quickly,” “happily,” “often,” “yesterday,” “here,” and “very.”
Examples:
Quickly (modifying the verb “ran”) – “She ran quickly to catch the bus.”
Happily (modifying the verb “smiled”) – “He smiled happily when he saw his friends.”
Often (modifying the verb “visit”) – “They often visit their grandparents on weekends.”
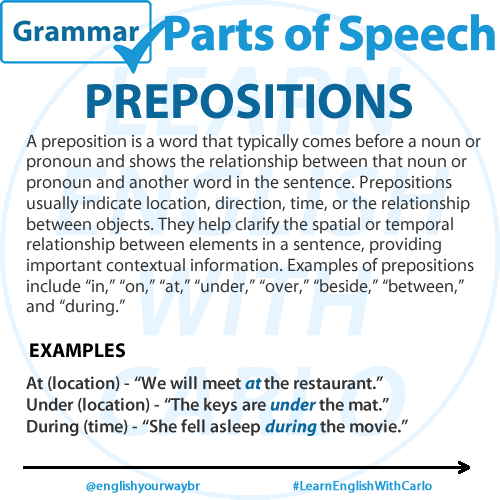
PREPOSITION
A preposition is a word that typically comes before a noun or pronoun and shows the relationship between that noun or pronoun and another word in the sentence. Prepositions usually indicate location, direction, time, or the relationship between objects. They help clarify the spatial or temporal relationship between elements in a sentence, providing important contextual information. Examples of prepositions include “in,” “on,” “at,” “under,” “over,” “beside,” “between,” and “during.”
Examples:
On (location) – “The book is on the table.”
Between (location) – “She stood between her two friends.”
At (location) – “We will meet at the restaurant.”
Under (location) – “The keys are under the mat.”
During (time) – “She fell asleep during the movie.”
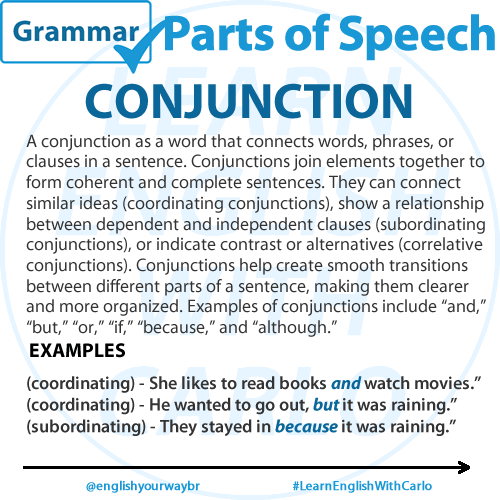
CONJUNCTION
A conjunction is a word that connects words, phrases, or clauses in a sentence. Conjunctions are important for joining elements together to form coherent and complete sentences. They can connect similar ideas (coordinating conjunctions), show a relationship between dependent and independent clauses (subordinating conjunctions), or indicate contrast or alternatives (correlative conjunctions). Conjunctions help create smooth transitions between different parts of a sentence, making the overall meaning clearer and more organized. Examples of conjunctions include “and,” “but,” “or,” “if,” “because,” and “although.”
Examples:
And (coordinating) – “She likes to read books and watch movies.”
But (coordinating) – “He wanted to go to the park, but it started raining.”
Because (subordinating) – “They stayed indoors because it was raining heavily.”
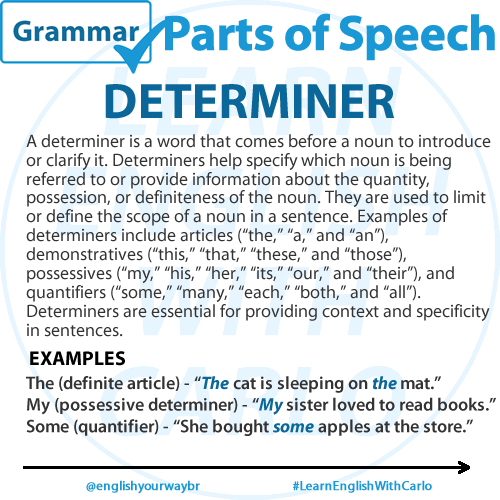
DETERMINER
A determiner is a word that comes before a noun to introduce or clarify it. Determiners help specify which noun is being referred to or provide information about the quantity, possession, or definiteness of the noun. They are used to limit or define the scope of a noun in a sentence. Examples of determiners include articles (such as “the,” “a,” and “an”), demonstratives (such as “this,” “that,” “these,” and “those”), possessives (such as “my,” “your,” “his,” “her,” “its,” “our,” and “their”), and quantifiers (such as “some,” “many,” “few,” “several,” “each,” “every,” “both,” “neither,” and “all”). Determiners are essential for providing context and specificity in sentences.
Examples:
The (definite article) – “The cat is sleeping on the mat.”
My (possessive determiner) – “My sister loves to read books.”
Some (quantifier) – “She bought some apples at the store.”
INTERJECTION
An interjection is a word or phrase that expresses emotion, feeling, or sudden reaction in a sentence. Interjections are often used to convey strong emotions such as joy, surprise, anger, pain, or relief. They can stand alone or be inserted into sentences to express the speaker’s immediate reaction or attitude. Interjections are not grammatically connected to other parts of the sentence and are usually followed by an exclamation mark to indicate their emotional intensity. Examples of interjections include “Wow!,” “Ouch!,” “Hey!,” “Oops!,” “Yikes!,” and “Hooray!” Interjections add color and expressiveness to language, allowing speakers to convey their emotions more vividly.
Examples:
Wow! (surprise or admiration) – “Wow! That magic trick was amazing!”
Ouch! (pain) – “Ouch! I stubbed my toe on the table.”
Yikes! (alarm or concern) – “Yikes! I forgot to turn off the stove!”