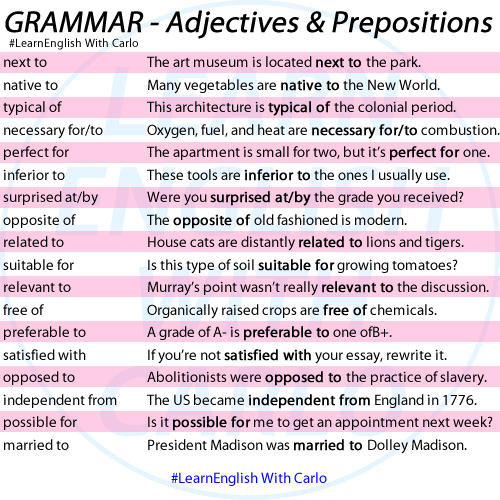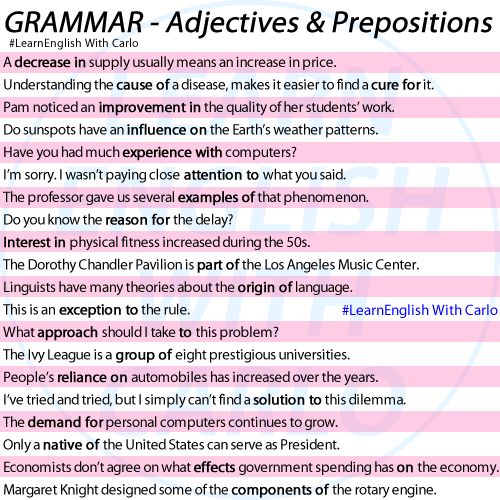
QUIT
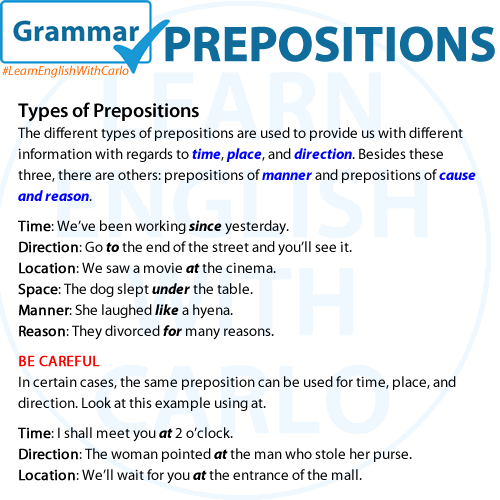
“Quit” is a verb that means to stop or cease doing something. When someone quits an activity, job, or habit, they discontinue or give up that particular action or commitment. “Quit” can also imply resignation or abandonment of a task or responsibility. It is often used in contexts related to work, sports, studies, or habits. For example, “He decided to quit his job and pursue a new career” or “She quit smoking last year.”
Examples:
She decided to quit her job and start her own business.
He couldn’t quit eating chocolate even though he knew it wasn’t good for him.
After years of struggling with the habit, he finally decided to quit smoking for good.

QUIET
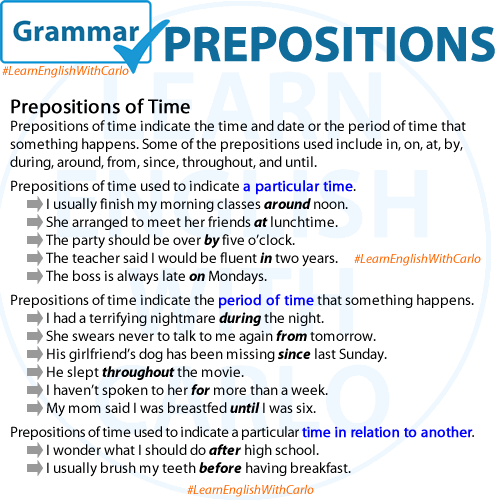
“Quiet” is an adjective that describes the absence of noise or disturbance, creating a peaceful or calm environment. It refers to a state of tranquility or minimal sound. Additionally, “quiet” can also be used as a verb, meaning to make something or someone become silent or less noisy. For example, “The library is a quiet place for studying,” or “Please quiet down so we can hear the speaker.”
Examples:
The baby finally fell asleep, and the house became quiet.
Please keep your voice down and try to be quiet during the movie.
The students were quiet in the classroom.

QUITE
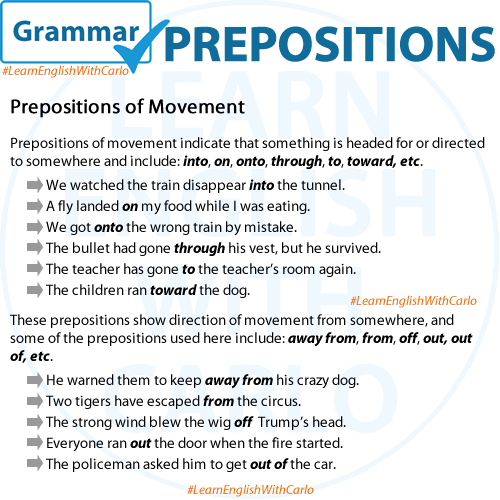
“Quite” as an adverb that is used to intensify the meaning of an adjective or adverb. It often indicates a degree or extent that is significant or noticeable. “Quite” can suggest a level of completeness, emphasis, or extent beyond what is expected. It can also indicate agreement or confirmation in response to a statement. For example, “She was quite tired after the long day” or “It’s quite hot outside today.”
Examples:
The hike was quite challenging, but we made it to the top.
She found the movie quite entertaining and watched it twice.
He was quite surprised when he received the award for his work.