Conjunctions: Linking Ideas with Clarity
Conjunctions are words used to connect ideas within the same sentence. Depending on the relationship between ideas, we use different conjunctions. Here are some common types, their meanings, and examples:
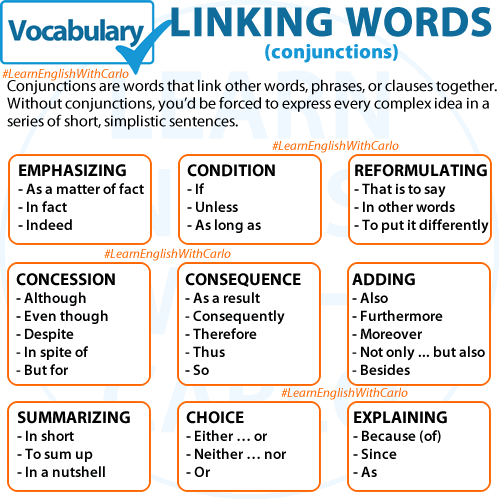
Emphasizing
Definition: Highlighting the importance of an idea.
Indeed: Reinforces a statement.
Example: This is a challenging project indeed.
As a matter of fact: Adds a surprising or clarifying fact.
Example: She’s not just talented; as a matter of fact, she’s a prodigy.
In fact: Provides evidence to support an idea.
Example: He looks young. In fact, he’s over 50.
Reformulating
Definition: Restating an idea for clarity.
To put it differently: Simplifies a statement.
Example: The project is delayed. To put it differently, we need more time.
That is to say: Clarifies or specifies a point.
Example: The car is electric, that is to say, it runs on batteries.
In other words: Explains an idea differently.
Example: He’s economical; in other words, he doesn’t like to spend money.
Summarizing
Definition: Condensing multiple ideas into a brief statement.
In a nutshell: Expresses the main idea concisely.
Example: In a nutshell, the movie was amazing.
In short: Summarizes key points.
Example: The meeting was long. In short, we decided to postpone the launch.
To sum up: Highlights conclusions.
Example: To sum up, teamwork is essential.
Condition
Definition: Indicates a requirement for something to happen.
As long as: Implies a condition is met.
Example: You can borrow the book as long as you return it tomorrow.
If: Introduces a condition.
Example: If it rains, we’ll stay indoors.
Unless: Suggests an exception.
Example: I won’t go unless you come with me.
Consequence
Definition: Shows the result of an action or event.
So: Simplifies cause and effect.
Example: I was tired, so I went to bed.
As a result: Indicates an effect.
Example: The roads were icy; as a result, the game was canceled.
Therefore: Highlights a logical conclusion.
Example: He was late; therefore, he missed the train.
Choice
Definition: Expresses alternatives.
Or: Presents options.
Example: Do you want tea or coffee?
Either … or: Indicates two possibilities.
Example: You can either walk or take the bus.
Neither … nor: Denies both options.
Example: He’s neither a doctor nor a lawyer.
Concession
Definition: Admits something unexpected.
Despite: Expresses contrast succinctly.
Example: We won the match despite our injuries.
Although: Contrasts ideas.
Example: Although it was raining, we went hiking.
Even though: Strengthens contrast.
Example: Even though she was tired, she stayed late to help.
Adding
Definition: Combines ideas for emphasis.
Moreover: Adds importance.
Example: The plan is practical. Moreover, it’s cost-effective.
Also: Adds information.
Example: She sings beautifully and also dances well.
Furthermore: Strengthens a point.
Example: The book is well-written. Furthermore, it’s inspiring.
Explaining
Definition: Provides reasons or causes.
As: Explains why something happens.
Example: I didn’t attend as I was feeling unwell.
Because (of): Shows the reason for something.
Example: We canceled the trip because of bad weather.
Since: Introduces a reason.
Example: Since it’s late, let’s go home.
