Learn how to pronounce the “-ed” sound at the end of a word.
Have you ever found yourself stumbling over the pronunciation of past tense verbs in English? You’re not alone. One of the trickiest aspects for non-native speakers (and sometimes native speakers too!) is mastering the pronunciation of the “-ed” ending. Fear not, as we embark on a journey to demystify this common linguistic hurdle.
Understanding the Basics
In English, regular verbs typically form their past tense by adding “-ed” to the base form of the verb. For example:
- Walk → Walked
- Talk → Talked
- Jump → Jumped
However, the way we pronounce the “-ed” ending can vary depending on the preceding sound.
Three Pronunciation Rules
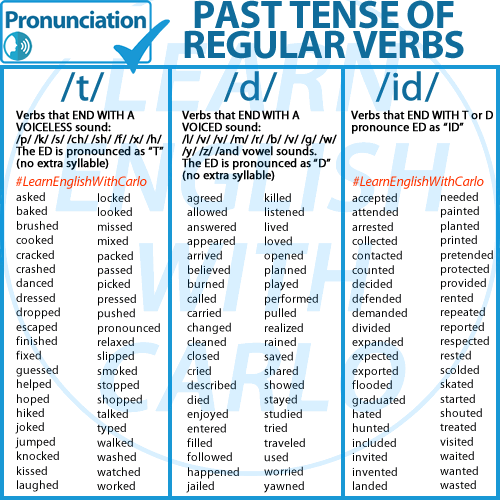
To simplify things, we can break down the pronunciation of “-ed” into three main rules:
Note: When you see letters or symbols between two slash marks (/ /), it refers to the pronunciation of that letter or sound.
1. /t/ Sound
When the base verb ends in a voiceless consonant sound (like /k/, /p/, /s/, /f/, /sh/, /ch/, etc.), the “-ed” ending is pronounced as a /t/ sound.
Examples:
- Walked (base form ends in /k/)
- Jumped (base form ends in /p/)
- Kissed (base form ends in /s/)
- Stopped (base form ends in /p/)
2. /d/ Sound
When the base verb ends in a voiced consonant sound (like /b/, /g/, /v/, /z/, /n/, /m/, /l/, etc.), the “-ed” ending is pronounced as a /d/ sound.
Examples:
- Lived (base form ends in /v/)
- Grabbed (base form ends in /b/)
- Jogged (base form ends in /g/)
- Buzzed (base form ends in /z/)
3. /ɪd/ Sound
When the base verb ends in a “t” or “d” sound, the “-ed” ending is pronounced as an extra syllable, /ɪd/.
Examples:
- Created (base form ends in /t/)
- Decided (base form ends in /d/)
- Needed (base form ends in /d/)
Practice Makes Perfect
While these rules provide a helpful framework, like many aspects of language, there are exceptions and irregularities. However, mastering the pronunciation of regular past tense verbs using these rules will significantly enhance your spoken English.
Tips for Practice:
- Listen and Repeat: Mimic native speakers by listening to how they pronounce past tense verbs in various contexts.
- Minimal Pairs: Practice distinguishing between similar sounds by using minimal pairs exercises. For example, listen to and repeat words like “kissed” and “kicked” to hone in on the differences in pronunciation.
- Record Yourself: Utilize technology to record yourself speaking and compare your pronunciation with native speakers. This can help you identify areas for improvement.
- Consistent Practice: Incorporate past tense verb pronunciation exercises into your regular English practice routine to reinforce your skills over time.
Conclusion
Navigating the pronunciation of past tense verbs in English can be challenging, but with awareness of the rules and consistent practice, you can significantly improve your spoken fluency. Remember, patience and persistence are key as you work towards mastering this aspect of the English language. Keep practicing, and before you know it, pronouncing “-ed” endings will become second nature. Happy learning!
