Conjunctions are essential parts of speech in English, connecting words, phrases, or clauses within a sentence. For ESL learners, understanding conjunctions is crucial for constructing clear and cohesive sentences. Conjunctions can be categorized into different types, each serving a specific purpose in expressing relationships between ideas.
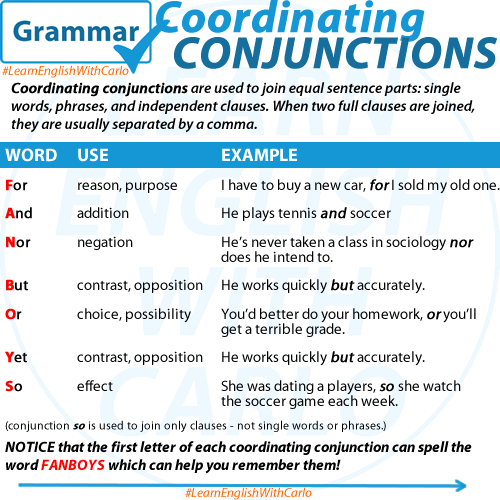
1. Coordinating Conjunctions: These conjunctions connect words, phrases, or clauses that are grammatically equal. The common coordinating conjunctions are “and,” “but,” “or,” “nor,” “for,” “yet,” and “so.” For example, “I like tea, but she prefers coffee.” Here, “but” connects two contrasting ideas.
2. Subordinating Conjunctions: These conjunctions introduce subordinate clauses, which cannot stand alone as complete sentences. Subordinating conjunctions indicate relationships such as time, cause and effect, contrast, and condition. Examples include “although,” “because,” “when,” “while,” “if,” and “since.” For instance, “I’ll go for a walk if the weather improves.”

3. Correlative Conjunctions: These conjunctions work in pairs to join similar sentence elements. Common correlative conjunction pairs include “either…or,” “neither…nor,” “both…and,” “not only…but also,” and “whether…or.” For example, “He can either come now or call later.”

Tips for ESL Learners:
- Learn the common conjunctions and their functions.
- Pay attention to the context in which conjunctions are used to understand their meaning better.
- Practice using conjunctions in sentences to express relationships between ideas effectively.
- Be aware of the difference between coordinating, subordinating, and correlative conjunctions and their appropriate usage in sentences.
