Mastering the simple past tense is an essential skill in English grammar. Regular verbs, which form the backbone of everyday communication, follow specific spelling rules when conjugated into the simple past tense. Understanding these rules empowers learners to express past actions accurately and confidently. In this blog post, we’ll explore the key spelling rules governing regular verbs in the simple past tense.
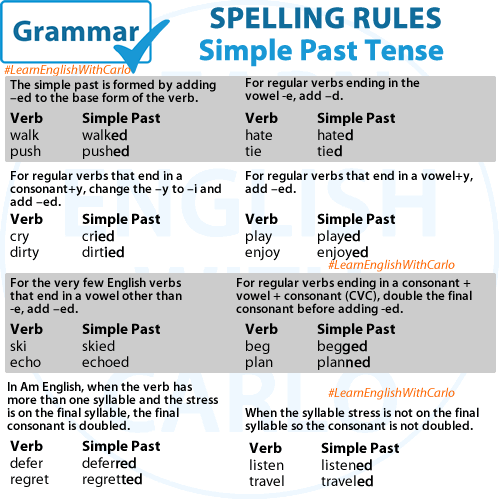
- Adding ‘-ed’ to Regular Verbs: The most common way to form the simple past tense of regular verbs is by adding ‘-ed’ to the base form of the verb. For example:
- Walk (base form) becomes walked (simple past)
- Talk (base form) becomes talked (simple past)
- Play (base form) becomes played (simple past)
- Spelling Rules for Adding ‘-ed’:
- Verbs ending in ‘-e’: If a regular verb ends in ‘e,’ simply add ‘-d’ to form the simple past tense.
- Example: Dance (base form) becomes danced (simple past)
- Verbs ending in a consonant + ‘y’: Change the ‘y’ to ‘i’ and add ‘-ed.’
- Example: Study (base form) becomes studied (simple past)
- Verbs ending in a single vowel + consonant: Double the final consonant before adding ‘-ed’ if the verb is one syllable and ends in a single vowel + consonant.
- Example: Stop (base form) becomes stopped (simple past)
- However, if the verb has more than one syllable or the final syllable is stressed, do not double the final consonant.
- Example: Visit (base form) becomes visited (simple past)
- Verbs ending in ‘-y’ following a consonant: Simply add ‘-ed’ without any changes.
- Example: Enjoy (base form) becomes enjoyed (simple past)
- Example: Enjoy (base form) becomes enjoyed (simple past)
- Verbs ending in ‘-e’: If a regular verb ends in ‘e,’ simply add ‘-d’ to form the simple past tense.
- Irregularities: While regular verbs generally follow these rules, it’s important to note that some verbs are irregular and do not conform to the standard ‘-ed’ ending. Examples of irregular verbs in the simple past tense include:
- Go (base form) becomes went (simple past)
- Eat (base form) becomes ate (simple past)
- See (base form) becomes saw (simple past)
- Practice Makes Perfect: Mastery of the simple past tense and its spelling rules comes with practice. Engage in activities such as reading, writing, and speaking to reinforce your understanding. Additionally, online resources and grammar exercises can provide targeted practice opportunities.
Conclusion: Understanding the spelling rules for regular verbs in the simple past tense is fundamental for effective communication in English. By following these guidelines and practicing regularly, learners can confidently express past actions with accuracy and fluency. Remember, consistency and persistence are key to mastering this essential aspect of English grammar.
