
Infinitives are the base form of a verb, usually preceded by “to” (e.g., to learn, to explore, to be). They’re incredibly versatile and are used in many ways to express purpose, intention, emotion, and more.
In this guide, we’ll break down the main uses of infinitives in English grammar, with examples that will make it easy to understand and use them in everyday situations.
🔤 What Is an Infinitive?
An infinitive is the base form of a verb, often introduced by the word “to.”
Examples:
- to run
- to eat
- to understand
- to be
Infinitives can act as nouns, adjectives, or adverbs, depending on how they’re used in a sentence.
🧩 1. Infinitive as a Subject

When an infinitive begins the sentence, it acts as the subject of the verb.
📌 Examples:
- To read is to open your mind.
- To travel broadens your perspective.
🧠 Tip: If you can replace the phrase with “something,” it’s probably a subject.
(E.g., Something broadens your perspective.)
🎯 2. Infinitive as a Direct Object
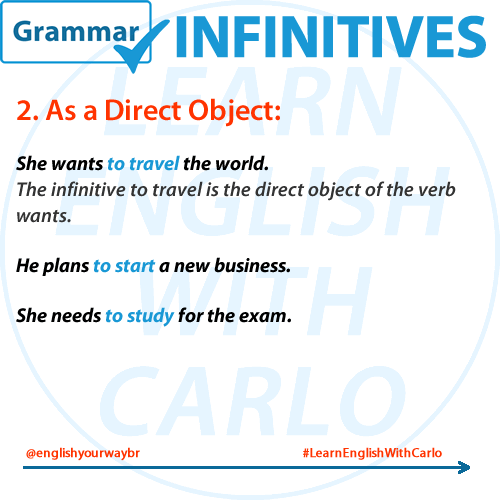
After some verbs, the infinitive functions as the direct object — the thing being acted upon.
📌 Examples:
- She loves to dance.
- He plans to study abroad.
Common verbs that are followed by infinitives include: want, hope, decide, learn, agree, need, promise, plan, expect.
💬 3. Infinitive as a Subject Complement

When used after a linking verb (like is, was, seems), the infinitive completes or renames the subject.
📌 Examples:
- Her dream is to write a novel.
- The goal is to finish on time.
🧱 4. Infinitive as an Adjective

Infinitives can describe a noun, acting like adjectives that give more information.
📌 Examples:
- I have a lot of things to do.
- There’s a book to read on the table.
Here, the infinitive tells us which things or book.
⏱️ 5. Infinitive as an Adverb
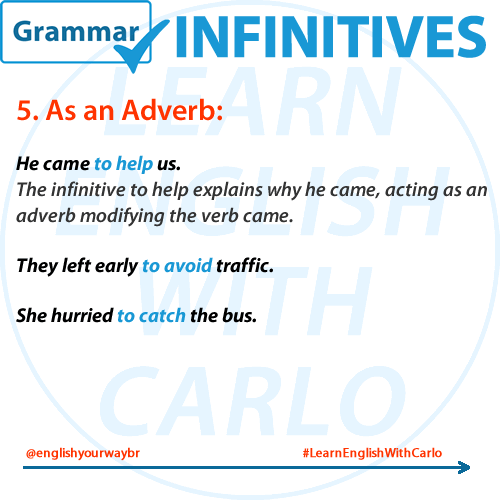
Infinitives can also describe why something is done — modifying a verb, adjective, or another adverb.
📌 Examples:
- They left early to catch the train.
- She studies hard to succeed.
These infinitives answer “Why?”.
🔗 6. Infinitive After Certain Verbs
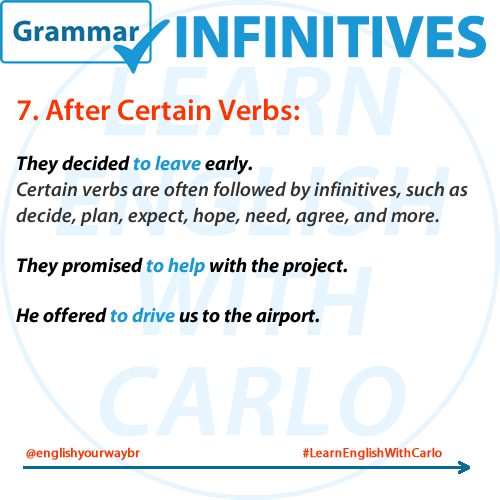
Some verbs are always followed by infinitives (never gerunds). These include: hope, decide, want, promise, agree, learn, need, refuse, plan.
📌 Examples:
- He promised to help with the project.
- They decided to join the class.
🛠️ 7. Infinitive to Show Purpose

This is one of the most common and useful uses of infinitives — to express purpose or reason for an action.
📌 Examples:
- She saved money to buy a new laptop.
- He practices daily to improve his skills.
🧠 Why did she save money? To buy something.
Why does he practice? To improve.
📝 Practice: Fill in the Blank with an Infinitive
- I want ___ a new language. (learn)
- She left work early ___ her child. (pick up)
- Their goal is ___ the tournament. (win)
- We need ___ harder next time. (try)
- This is a problem ___ quickly. (solve)
Answers:
- to learn
- to pick up
- to win
- to try
- to solve
📌 Summary Chart: Uses of Infinitives
| Use | Example |
|---|---|
| Subject | To learn English is important. |
| Direct Object | He wants to travel. |
| Subject Complement | The goal is to win. |
| Adjective | I have homework to finish. |
| Adverb | She runs to stay healthy. |
| After Certain Verbs | They agreed to help. |
| To Show Purpose | He studies to pass the test. |
✅ Conclusion
Infinitives are essential tools in English grammar. They help you express actions, goals, purposes, and feelings clearly and effectively. With a bit of practice, you’ll be using infinitives like a pro!
