When to Use the Simple Past Tense

The Simple Past is used to talk about actions, events, or states that were completed in the past. Here are the main situations when we use the Simple Past:
- Completed Actions in the Past:
- We use the Simple Past for actions that started and finished in the past. There is usually a time reference (yesterday, last week, etc.).
- Example: I visited Paris last summer.
- Series of Completed Actions:
- The Simple Past can be used to list a series of actions that happened one after another.
- Example: She opened the door, walked in, and sat down.
- Habits in the Past:
- For repeated actions or habits in the past, we use the Simple Past.
- Example: When I was a child, I played outside every day.
- States in the Past:
- We also use the Simple Past to describe past states or conditions.
- Example: The house was old and needed repairs.
How to Form the Simple Past Tense
The formation of the Simple Past depends on whether the verb is regular or irregular.
1. Regular Verbs:
Regular verbs in the Simple Past are formed by adding -ed to the base form of the verb.
- Affirmative Form:
- Subject + base verb + -ed
- Example: He worked late last night.
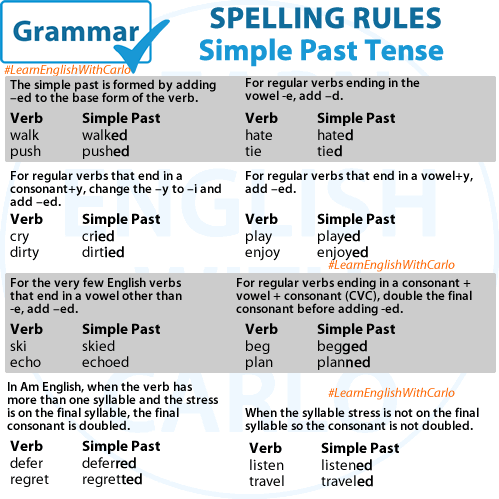
- Spelling Rules for Regular Verbs:
- Verbs that end in -e: just add -d (e.g., live → lived, love → loved).
- Verbs that end in a single vowel + single consonant: double the final consonant and add -ed (e.g., stop → stopped, plan → planned).
- Verbs that end in -y:
- If the verb ends in a consonant + -y, change the -y to -i and add -ed (e.g., try → tried, cry → cried).
- If the verb ends in a vowel + -y, just add -ed (e.g., play → played).
- Negative Form:
- Subject + did not (didn’t) + base form of the verb
- Example: She didn’t work yesterday.
- Question Form:
- Did + subject + base form of the verb?
- Example: Did they watch the movie?
2. Irregular Verbs:
Irregular verbs do not follow a set pattern in the Simple Past. Their forms must be memorized. Here are some common examples:
| Base Form | Simple Past |
|---|---|
| go | went |
| have | had |
| buy | bought |
| eat | ate |
| come | came |
| see | saw |
- Affirmative Form:
- Subject + irregular verb (past form)
- Example: She went to the store.
- Negative Form:
- Subject + did not (didn’t) + base form of the verb
- Example: They didn’t go to the store.
- Question Form:
- Did + subject + base form of the verb?
- Example: Did you eat dinner?
Examples with Regular and Irregular Verbs:
- Regular Verb (to work):
- Affirmative: She worked yesterday.
- Negative: She didn’t work yesterday.
- Question: Did she work yesterday?
- Irregular Verb (to go):
- Affirmative: They went to the park.
- Negative: They didn’t go to the park.
- Question: Did they go to the park?
Pronunciation of -ed Endings
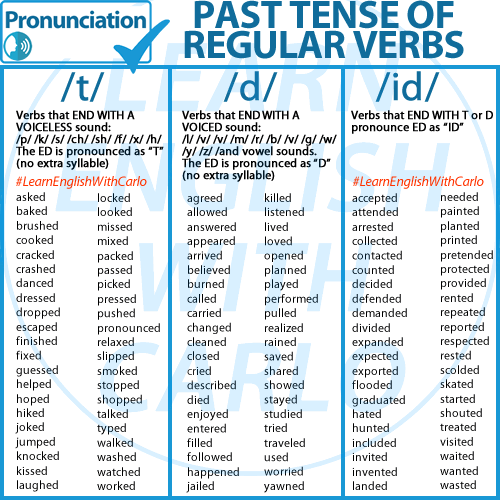
Regular verbs in the Simple Past have three different pronunciations of -ed, depending on the final sound of the base verb.
- /t/ sound: When the base verb ends in a voiceless sound (e.g., p, k, f, s, sh, ch, x).
- Example: helped, asked, laughed
- /d/ sound: When the base verb ends in a voiced sound (e.g., b, g, l, m, n, v, z, r, vowels).
- Example: cleaned, played, saved
- /ɪd/ sound: When the base verb ends in -t or -d.
- Example: wanted, needed, started
Common Time Expressions Used with the Simple Past
- Specific Times in the Past: yesterday, last week, in 2001, two days ago, at 7 o’clock.
- Duration in the Past: for two years, all morning, from 1990 to 1995.
- Finished Time Periods: when I was a child, in the past, once upon a time.
