English has several ways to express the future, and each method is used in different situations. Here are the most common ways to talk about future actions, events, or situations.
1. Future with “Will”
When to Use “Will”
- Predictions about the future (things you think will happen):
- Example: It will rain tomorrow.
- Decisions made at the moment of speaking (spontaneous decisions):
- Example: I’m hungry. I think I will order a pizza.
- Promises, offers, and requests:
- Example: I will help you with your homework.
- Example: Will you marry me?
- Future facts (something that is certain):
- Example: The sun will rise at 6 AM.
Grammar Rule:
- Affirmative:
Subject + will + base verb
Example: She will call you later. - Negative:
Subject + will not (won’t) + base verb
Example: I won’t forget your birthday. - Question:
Will + subject + base verb?
Example: Will they arrive on time?
2. Future with “Going to”
When to Use “Going to”
- Plans and intentions: When you’ve already decided to do something:
- Example: I’m going to start a new job next week.
- Predictions based on present evidence: When you see something happening:
- Example: Look at those clouds. It’s going to rain.
Grammar Rule:
- Affirmative:
Subject + am/is/are going to + base verb
Example: They are going to travel to Spain. - Negative:
Subject + am not/isn’t/aren’t going to + base verb
Example: He isn’t going to study tonight. - Question:
Am/Is/Are + subject + going to + base verb?
Example: Are you going to attend the meeting?
3. Future with the Present Continuous
When to Use the Present Continuous for the Future
- Arrangements: When you have arranged or scheduled something, often with other people:
- Example: I’m meeting Sarah tomorrow at 10 AM.
- Definite plans: When something is set to happen soon:
- Example: We’re leaving for the airport in an hour.
Grammar Rule:
- Affirmative:
Subject + am/is/are + verb-ing
Example: She is having dinner with her friends tonight. - Negative:
Subject + am not/isn’t/aren’t + verb-ing
Example: They aren’t visiting the museum tomorrow. - Question:
Am/Is/Are + subject + verb-ing?
Example: Are you meeting John after work?
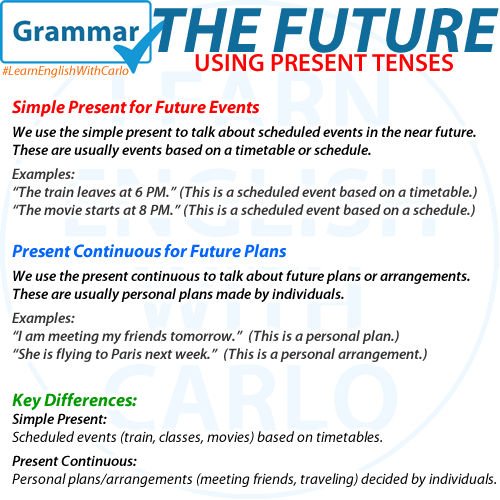
4. Future with the Present Simple
When to Use the Present Simple for the Future
- Scheduled events: This is used when talking about timetables, schedules, or events that are part of a fixed program (e.g., transportation, events, formal schedules):
- Example: The train leaves at 9:30 AM tomorrow.
- Example: The meeting starts at 3 PM.
Grammar Rule:
- Affirmative:
Subject + base verb
Example: The movie starts at 7 PM. - Negative:
Subject + do/does not + base verb
Example: The flight doesn’t depart until 10 PM. - Question:
Do/Does + subject + base verb?
Example: Does the store open at 9 AM tomorrow?
Summary: When to Use Each Form
| Future Form | Use Cases | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Will | Predictions, spontaneous decisions, promises | I will call you later. |
| Going to | Plans and intentions, predictions based on evidence | I’m going to visit my grandparents. |
| Present Continuous | Arranged or scheduled actions | She is meeting her boss tomorrow. |
| Present Simple | Timetables, scheduled events | The plane leaves at 6 PM. |
